අපි ECG කියවමු.. 1 කොටස How to read ECG basic rhythm in sinhala
HTML-код
- Опубликовано: 6 фев 2021
- A basic ECG rhythm, also known as normal sinus rhythm, represents the standard electrical activity of a healthy heart. Here's a detailed description of the key components of a basic ECG rhythm:
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR):
Origin: Originates from the sinoatrial (SA) node, the natural pacemaker of the heart, which is located in the right atrium.
Rate: The normal heart rate typically falls between 60 and 100 beats per minute in adults.
Steady Rhythm: Regular and consistent timing between heartbeats.
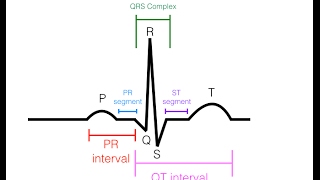
P Wave:
Description: The P wave is the first upward deflection on the ECG.
Significance: Represents atrial depolarization, indicating the contraction of the atria.
Normal Duration: Usually less than 0.12 seconds.
PR Interval:
Definition: Measured from the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex.
Significance: Represents the time taken for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
Normal Duration: Typically between 0.12 and 0.20 seconds.
QRS Complex:
Description: The QRS complex is the combination of the Q, R, and S waves.
Significance: Represents ventricular depolarization, indicating the contraction of the ventricles.
Normal Duration: Usually less than 0.12 seconds.
QT Interval:
Definition: Measured from the beginning of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave.
Significance: Represents the total time for ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
Normal Duration: Varies with heart rate; a corrected QT (QTc) is often used for comparison.
T Wave:
Description: The T wave is the upward deflection following the QRS complex.
Significance: Represents ventricular repolarization, indicating the relaxation of the ventricles.
Normal Characteristics: Usually in the same direction as the QRS complex but smaller.
In summary, a basic ECG rhythm, or normal sinus rhythm, is characterized by a regular heartbeat originating from the SA node, with distinct P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves. The intervals between these components fall within normal ranges. Any deviations from this pattern may indicate underlying cardiac issues, and a healthcare professional should interpret and analyze the ECG results for a comprehensive assessment of heart
ecg,ekg,ecg interpretation,ekg interpretation,ecg interpretation made easy,nursing school,nursing








Super, thanks
Thanks you
Thank you very much ayye🙂🙂🙂
super sir. thank you so much. i am watching this after asking blame from by my consultant because not knowing how to interpret ecg. so this is very valuable for us sir
😊😊😊 you are welcome
Please can you do physics and measurement topics
Good explanation
මරු ❤
Great explanation thank you
You are welcome!
💯👌
Docor u explained very wel..thank you very much
You are welcome
Ammoooo...hina unaa..igenath gatta..the best teacher ❤
Thank you
😁 thank you doctor
Dyyo inna thannam waradiii . Incorrect chest leads placement.
Can you do ECG lectures in English
Great
Thank you
Super❤️❤️❤️
Thank you
Good job. All the best Dinusha.
Thank you machan
❤️❤️
🙂🙂
English please
sir i work in the private biomedical field , sir great explanation , let me more correct you v1 , v2 placement it should be 4 th intercostal line , thank you, sir please talk about arrithmia conditions and reasons , anti arrythmic drugs , their ecg changes and explanations to those changes , also talk about right side ecg placement and patterns , ..............etc
Thank you waruna
❤❤❤❤❤
Thank you❤
Ube CCTV eka monapeththatada harawala thibune
අාාා 😟😛😛😛😛
ශෝක් නේ ,
හිනාවුනා ,
එතකොට අනිත් ටික කියලා දෙන්නේ කවුද ?
So do RS and CVS too.
දෙවැනි කොටසෙන්😂😂😂🙂🙂🙂🤗🤗
Ok i will do 😊😊🤗
Super, thanks