Physiology of heart part 1
HTML-код
- Опубликовано: 5 фев 2025
- #foryou #trending #trending #medical #physiology
Physiology of heart ( cardio physiology ) lecture by Ruqaiya Farooq Medsparkles.
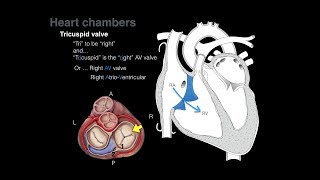
The oscillation is that the performance of the human heart from the start of 1 heartbeat to the start of future. It consists of 2 periods: one throughout that the center muscle relaxes and refills with blood, known as pulse, following a amount of sturdy contraction and pumping of blood, dubbed heartbeat. once voidance, the center now relaxes and expands to receive another flow of blood getting back from the lungs and different systems of the body, before once more getting to pump blood to the lungs and people systems. A ordinarily acting heart should be totally swollen before it will expeditiously pump once more. presumptuous a healthy heart and a typical rate of seventy to seventy five beats per minute, every oscillation, or heartbeat, takes regarding zero.8 seconds to finish the cycle.[2] There area unit 2 chamber and 2 ventricle chambers of the heart; they're paired because the left heart and also the right heart-that is, the left atrium of the heart with the heart ventricle, the proper atrium with the proper ventricle-and they add concert to repeat the oscillation endlessly, (see cycle diagram at right margin). At the beginning of the cycle, throughout cavity diastole-early, the center relaxes and expands whereas receiving blood into each ventricles through each atria; then, close to the tip of cavity diastole-late, the 2 atria begin to contract (atrial systole), and every atrium pumps blood into the ventricle below it.[3] throughout cavity heartbeat the ventricles area unit getting and smartly pulsing (or ejecting) 2 separated blood provides from the heart-one to the lungs and one to any or all different body organs and systems-while the 2 atria area unit relaxed (atrial diastole). This precise coordination ensures that blood is expeditiously collected and circulated throughout the body.[4]
The mitral and angulate valves, conjointly referred to as the chamber, or Jewish calendar month valves, open throughout cavity pulse to allow filling. Late within the filling amount the atria begin to contract (atrial systole) forcing a final crop of blood into the ventricles underneath pressure-see cycle diagram. Then, prompted by electrical signals from the cardiac muscle, the ventricles begin getting (ventricular systole), and as back-pressure against them will increase the Jewish calendar month valves area unit forced to shut, that stops the blood volumes within the ventricles from flowing in or out; this can be referred to as the isovolumic contraction stage.
Now follows the isovolumic relaxation, throughout that pressure at intervals the ventricles begin to fall considerably, and thenceforth the atria begin replenishment as blood returns to flow into the proper atrium (from the blood vessel cavae) and into the left atrium of the heart (from the pneumonic veins). because the ventricles begin to relax, the mitral and angulate valves open once more, and also the completed cycle returns to cavity pulse and a replacement "Start" of the oscillation.
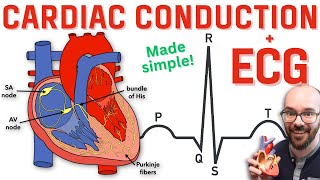
In Associate in Nursing graphical record, electrical heartbeat initiates the chamber heartbeat at the P wave deflection of a gentle signal; and it starts contractions (systole).
Cardiac cycle



![Seungmin "그렇게, 천천히, 우리(As we are)" | [Stray Kids : SKZ-PLAYER]](http://i.ytimg.com/vi/kAzmhLHePqU/mqdefault.jpg)

![Noob To Max With DRAGON REWORK In Blox Fruits [FULL MOVIE]](http://i.ytimg.com/vi/LnBMOinoOvA/mqdefault.jpg)
