Hybridization Chemistry
HTML-код
- Опубликовано: 11 фев 2025
- Hybridization Chemistry
For Live Classes, Concept Videos, Quizzes, Mock Tests & Revision Notes please see our Website/App:
Our Website: bit.ly/2KBC0l1
Android App: bit.ly/3k48zdK
CBSE Class 11 Courses: bit.ly/48isN9Q
CBSE Class 10 Courses: bit.ly/363U55V
CBSE Class 9 Courses: bit.ly/39Pm7mM
CBSE Class 8 Courses: bit.ly/3bJByzB
ICSE Class 10 Courses: bit.ly/2MaXpFo
ICSE Class 9 Courses: bit.ly/3iFV7dl
ICSE Class 8 Courses: bit.ly/3boM5OB
IGCSE Courses: bit.ly/2YNwQcn
Artificial Intelligence: bit.ly/3vm3FAE
Python Coding: bit.ly/3nX0s2y
Java Coding: bit.ly/3chHTAK
Facebook page: bit.ly/2s6VYhf
Hybridization in chemistry is a concept used to explain the bonding in molecules. It involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals that can then form covalent bonds with other atoms. Here's a more detailed explanation:
1. Atomic Orbitals: Atoms have orbitals (s, p, d, f) where electrons are likely to be found. These orbitals have different shapes and energies.
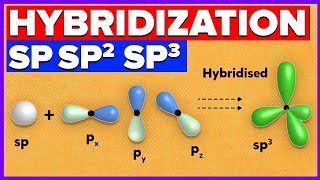
2. Mixing of Orbitals: When atoms form molecules, the atomic orbitals of the bonding atoms can mix or hybridize to form new orbitals. These new orbitals are called hybrid orbitals.
3. Types of Hybridization:
sp Hybridization: One s orbital mixes with one p orbital to form two sp hybrid orbitals. This occurs in molecules with linear geometry, like BeCl₂.
sp² Hybridization: One s orbital mixes with two p orbitals to form three sp² hybrid orbitals. This occurs in molecules with trigonal planar geometry, like BF₃.
sp³ Hybridization: One s orbital mixes with three p orbitals to form four sp³ hybrid orbitals. This occurs in molecules with tetrahedral geometry, like CH₄.
sp³d Hybridization: One s orbital mixes with three p orbitals and one d orbital to form five sp³d hybrid orbitals. This occurs in molecules with trigonal bipyramidal geometry, like PCl₅.
sp³d² Hybridization: One s orbital mixes with three p orbitals and two d orbitals to form six sp³d² hybrid orbitals. This occurs in molecules with octahedral geometry, like SF₆.
4. Bond Formation: The hybrid orbitals overlap with orbitals from other atoms to form covalent bonds. The shape and orientation of these hybrid orbitals determine the geometry of the molecule.
Hybridization helps explain the shape of molecules, bond angles, and the distribution of electrons in molecules, providing a more accurate description than using only atomic orbitals.
At Manocha Academy, learning Science and Math is Easy! The school coursework is explained with simple examples that you experience every day! Yes, Science & Math is all around you! Let's learn every day from everyday life!